3D Brain Model: Revolutionizing Medical Education
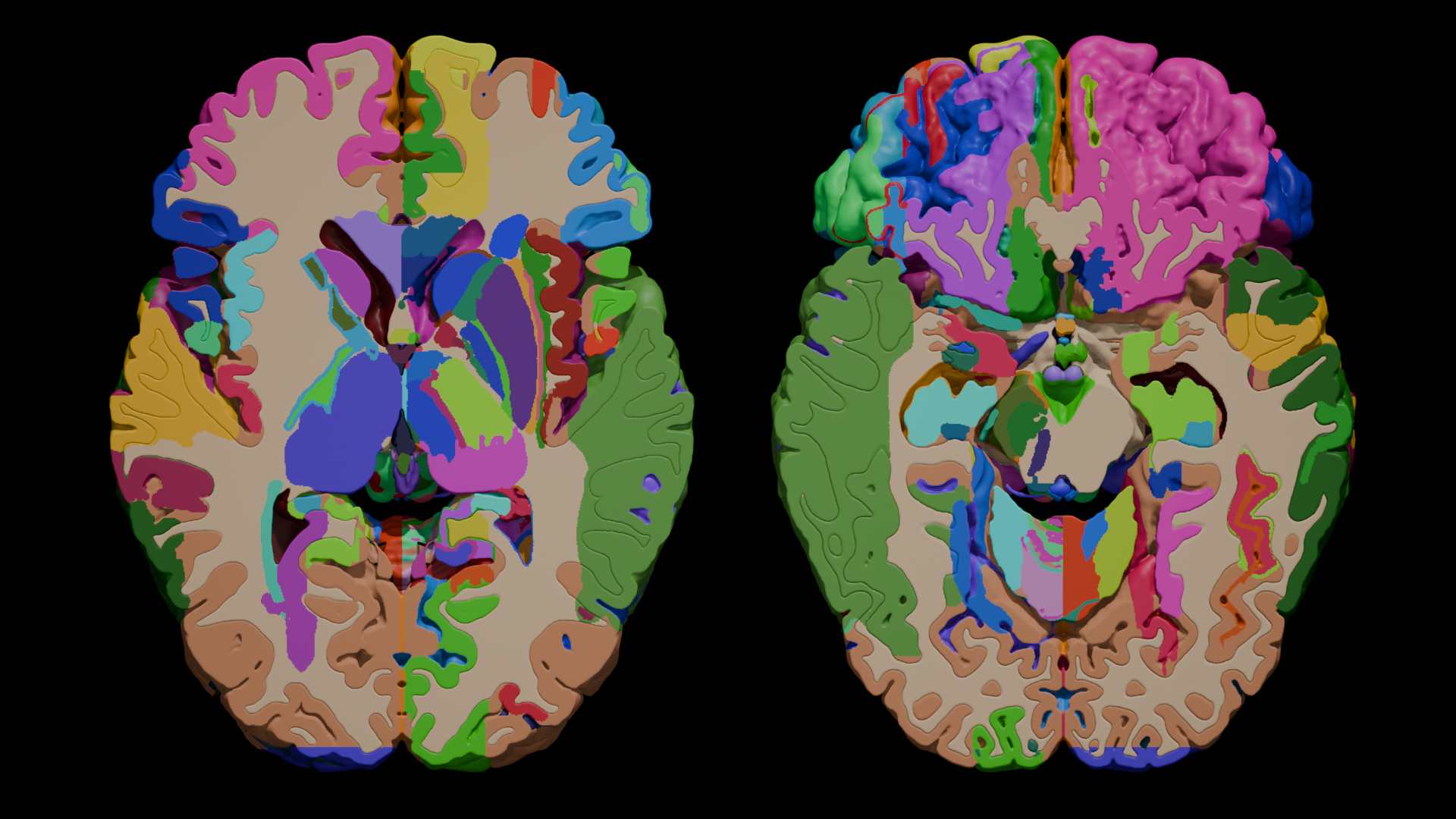
The evolution of the 3D Brain Model has redefined how medical students approach the complex subject of human brain anatomy. With high-fidelity, interactive brain model platforms and physical anatomical models, students are now better equipped than ever to grasp the nuances of brain structures, brain region functions, and detailed brain features. Whether using a 2-Part Brain Model, 5-Part Brain Model, or 8-Part Brain Model, learners can now visualize and understand components like the Cerebrum, Cerebellum, Brain Stem, and Hypothalamus more effectively.
Brain Models for Learning Complex Structures
Modern brain anatomy models provide medical students with tangible access to essential areas of the human brain. These models detail the Frontal Lobe, Temporal Lobe, Parietal Lobe, and Occipital Lobe, all vital in comprehending brain functions. High-end options such as 3B Scientific Brain Models and other scientific brain models are used extensively in classrooms and labs to teach the brain’s gray matter, white matter, and nervous tissue composition.
These functional brain models incorporate clear representations of the Thalamus, Fornix, Substantia Nigra, Basal Ganglia, and Heschl’s Gyrus, which are essential for understanding brain activity and related brain disorders. Additionally, they often integrate brain pathology models that highlight the impact of disease on brain tissue and brain cells.
Meninges and Internal Protection of the Brain
One of the more overlooked yet crucial topics covered in brain anatomy lessons is the study of the Meninges. These three layers of protective tissue safeguard the human brain, surrounding the cerebral cortex and other vital areas like the pineal gland and Cerebral Aqueducts. By using anatomical teaching models, students learn how these membranes maintain the brain’s structural and physiological integrity.
Detailed 3D visuals also demonstrate how the Meninges interact with the brain’s control center, influencing the central nervous system. Accompanying tools like the C15 Model, C18 Model, and C22 Model provide deeper insight into internal anatomy, allowing for comprehensive understanding from both macroscopic and microscopic perspectives.
Physical 3D Brain Models: Tactile Learning Tools
Physical 3D brain models remain an essential resource for medical students. Unlike virtual tools, these models offer tactile learning through components such as the brain lobes, Cerebrum, Cerebellum, and Brain Stem. Anatomical replicas like the head brain model are crucial in demonstrating real-world relationships among various brain parts.
These detailed brain models are often accurate anatomical models derived from the actual human brain, designed for clarity and precision. They may also highlight features like the Encephalic Trunk, Wernicke Area, and Broca Area, providing a hands-on understanding of language centers and learning brain activities. The C25 Model, in particular, serves as an advanced instructional tool for both gross and subtle brain structures.
Interactive 3D Brain Models in Modern Classrooms
Digital tools such as interactive 3D brain models have further expanded the reach of neuroscience education. These platforms allow users to explore a 3D Brain Model interactively, manipulate layers, and isolate specific brain features such as the cerebral cortex and brain nerves. Many applications are designed to highlight the brain’s memory, brain controls, and different sections of gray matter and white matter.
These technologies represent a shift in educational strategy, providing medical students with a dynamic alternative to traditional lectures. By including neuro-anatomical model simulations, students get a more accurate representation of how brain designs relate to neurological function and pathology. These innovations also include virtual walkthroughs of ventricles, Hypothalamus, and brain region functions for advanced understanding.
Anatomy Models and Digital Anatomy Solutions: Shaping the Future of Learning
The combination of digital anatomy solutions and traditional anatomy models is reshaping how anatomy is taught and learned. Platforms like BioDigital Human and Visible Body Human provide extensive libraries of interactive anatomy content, including relief models, joint models, and other anatomic model solutions.
These modern tools allow educators to offer a rich, immersive learning experience, with detailed anatomy interactive atlases and customizable interactive 3D anatomy models that cover the full spectrum of body anatomy. The integration of digital anatomy with physical printed anatomic models ensures students gain a thorough, hands-on understanding of human anatomy.
3D Brain Model as an Educational Standard
The adoption of the 3D Brain Model in classrooms is not just a trend but a standard in contemporary medical training. Paired with brain anatomy models and interactive brain model platforms, these resources empower medical students to navigate complex subjects like brain disorders, basic brain anatomy, and brain cells with confidence.
Whether exploring the cerebellum brain stem, Meninges, or brain anatomy, students benefit from immersive, multi-sensory learning experiences. These three-dimensional brain models provide unparalleled clarity and engagement, bringing the study of the human brain into a new era of education.
Conclusion
In summary, the high-fidelity 3D Brain Model—with both digital and physical 3D brain models—has transformed how medical students learn. It offers access to the most intricate details of the human brain anatomy, from the Frontal Lobe and Temporal Lobe to the Thalamus and Cerebrum, setting the foundation for the next generation of medical professionals.



